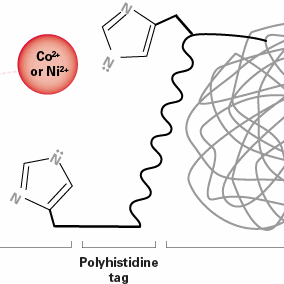
How to choose the right his-tagged purification resin
In the grand scheme of your research, the resin you use to purify your construct seems like one of the more trivial decisions. After all, the resin your labmate uses seems to work great. However, every protein construct is a little different, so the resin that works for the rest of your lab may not be the right one for your project. His-tagged proteins are purified using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) resins, which come in many flavors of metal cores—the most popular being nickel- (Ni2+) or cobalt-based (Co2+) resins. Which one is the right choice for your next his-tagged protein purification? The answer lies in determining whether yield or purity is more crucial for your downstream applications.
The differences in performance of Co2+- and Ni2+-based IMAC resins is a result of the spatial positioning of each metal ion in the reactive core influencing the specificity and capacity of histidine binding (because, as all protein researchers know, structure impacts function!) Cobalt-based resins offer better specificity, resulting in higher purity, while nickel-based resins offer better adsorption, resulting in higher binding capacity. Each type of resin has its advantages and limitations, depending on your specific application.

Cobalt-based resin
|
Advantages
|
Applications
|

The reactive core of a cobalt-based resin has strict requirements for the spatial positioning of histidines, so only proteins containing adjacent histidines or specially positioned neighboring histidines are able to bind cobalt in this reactive core, resulting in higher purity and lower yields. Use a cobalt-based resin if you need extremely pure protein for highly sensitive methods such as crystallography and functional assays.
Nickel-based resin
|
Advantages
|
Applications
|

The reactive core of a nickel-based resin has less strict spatial requirements, so it binds histidines located in places other than the protein's polyhistidine tag, resulting in higher yields and lower purity. Nickel-based resins are commonly available with iminodiacetic acid (IDA) and nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) as the chelating ligand, which differ in how strongly they coordinate with the metal ion. IDA has three coordination sites with the Ni2+ ion, leaving three open sites for histidine residues to interact with the ion. NTA, on the other hand, has four coordination sites with the Ni2+ ion, leaving only two sites for histidine residues. Therefore, IDA-based resins have higher binding capacities. However, it is critical to note that the weaker coordination between IDA and the Ni2+ ion also leads to an increased likelihood of leaching of the metal into the purification buffers, which can negatively impact some downstream applications. If your main objective is to purify large amounts of protein for labeling experiments and antibody production, then a nickel-based resin is the better choice.
Summary
As an early step in protein research, choosing the right IMAC resin for your his-tagged protein purification is essential for achieving the best results for your downstream applications. It is difficult to predict which resin will work best for a given construct ahead of time, so the best approach is typically to test a few resins in small-scale batch purifications and assess which combination of yield and purity works best for your situation. To learn more about choosing the best his-tagged protein purification method for your experiment, read our his-tagged protein purification overview.
Capturem technology
There is a constant need for faster, more efficient antibody and protein purification processes at any scale. Capturem membrane technology allows for purification directly from complex matrices, such as cell supernatants, in minutes. This technology also provides highly purified and concentrated antibodies and his-tagged proteins, even from samples containing additives not compatible with other purification technologies.
Antibody purification His-tagged purificationTakara Bio USA, Inc.
United States/Canada: +1.800.662.2566 • Asia Pacific: +1.650.919.7300 • Europe: +33.(0)1.3904.6880 • Japan: +81.(0)77.565.6999
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES. © 2025 Takara Bio Inc. All Rights Reserved. All trademarks are the property of Takara Bio Inc. or its affiliate(s) in the U.S. and/or other countries or their respective owners. Certain trademarks may not be registered in all jurisdictions. Additional product, intellectual property, and restricted use information is available at takarabio.com.