Our Matchmaker systems are highly advanced tools for identifying and characterizing novel protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Our latest and most powerful incarnation, the Matchmaker Gold Yeast Two-Hybrid System, adds a sensitive Aureobasidin A (AbA; Takesako et al. 1991) antibiotic resistance marker to two nutritional reporters and blue/white color selection. This results in a four-reporter system with the easiest, most stringent yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) screening strategy available (Figure 1).
Aureobasidin A effectively kills yeast, but when the AUR1-C gene is turned on by a positive interaction between GAL4-hybrid proteins, the yeast become AbA-resistant. Secondary confirmation of positive clones employs four reporters regulated by three different GAL4-responsive promoters. This effectively eliminates false positives and leaves you with greater numbers of genuine positives. Quality screening results like these, as well as our simple Mate & Plate library screening protocol, save you time and make your search for PPIs faster, easier, and more fruitful.

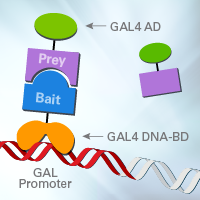
Figure 1. Yeast two-hybrid system design. Library-derived, transcription-activating prey fusion proteins that interact with the DNA-binding bait fusion protein activate the expression of reporter genes.
Y2H systems exploit the modular nature of eukaryotic transcription factors, which consist of a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain (DNA-BD) and an RNA Pol II-recruiting transcription activation domain (AD; Fields and Song 1989; Chien et al. 1991). In Matchmaker systems, a known protein of interest is fused to the DNA-BD of the yeast GAL4 transcription factor to create a “bait” protein. Interacting partner proteins, often derived from a library, are expressed as fusions to the AD of yeast GAL4, to create “prey” proteins (Figure 1). When pairs of interacting bait and prey fusion proteins are coexpressed in a yeast cell, GAL4 function is restored and the interacting fusion proteins are able to activate transcription of the reporter genes. In Matchmaker Gold, yeast clones that harbor interacting protein pairs can then be identified by the presence of the four reporters (Figure 2). In library screens, the plasmids containing the coding sequences for the library-derived prey proteins can be rescued from the surviving yeast clones and subjected to further analysis and sequencing.

Figure 2. Four reporters give Matchmaker Gold its high stringency. Interacting bait and prey fusion proteins drive the expression of four different reporters from three different GAL4-responsive promoters (M1, G1, and G2), which are stably integrated in the genome of the reporter strain, Y2HGold. AbA resistance and the two auxotrophic reporters for histidine and adenine biosynthesis confer growth selection in the presence of AbA and on histidine- and adenine-deficient media, while the α-galactosidase reporter produces blue colonies in the presence of X-alpha-Gal.